2020 Economic Stimulus Package
Ian Campbell • 23 March 2020
ECONOMIC STIMULUS PACKAGE (COVID-19)
On 12.3.2020, the Federal Government announced a $17.6 billion economic plan to keep Australians in jobs, keep businesses in business and support households and the Australian economy as the world deals with the significant challenges posed by the spread of the coronavirus.
The targeted stimulus package is focused on keeping Australians in jobs and helping small and medium sized businesses to stay in business.
The package has four parts:
Supporting business investment
Providing cash flow assistance to help small and medium sized business to stay in business and keep their employees in jobs
Targeted support for the most severely affected sectors, regions and communities;
Household stimulus payments that will benefit the wider economy
According to Prime Minister Scott Morrison the measures are all temporary, targeted and proportionate to the challenge we face.
The actions will ensure we respond to the immediate challenges we face and help Australia bounce back stronger on the other side, without undermining the structural integrity of the Budget.
As part of the plan up to 6.5 million individuals and 3.5 million businesses would be directly supported by the package.
Delivering support for business investment
$700 million to increase the instant asset write off threshold from $30,000 to $150,000 and expand access to include businesses with aggregated annual turnover of less than $500 million (up from $50 million) until 30 June 2020. For example, assets that may be able to be immediately written off are a concrete tank for a builder, a tractor for a farming business, and a truck for a delivery business.
$3.2 billion to back business investment by providing a time limited 15 month investment incentive (through to 30 June 2021) to support business investment and economic growth over the short term, by accelerating depreciation deductions. Businesses with a turnover of less than $500 million will be able to deduct an additional 50 per cent of the asset cost in the year of purchase.
These measures commenced on 12.3.2020 and will support over 3.5 million businesses (over 99 per cent of businesses) employing more than 9.7 million employees or 3 in every 4 workers. The measures are designed to support business sticking with investment they had planned, and encouraging them to bring investment forward to support economic growth over the short term.
Cash flow assistance for businesses
$6.7 billion to Boost Cash Flow for Employers by up to $25,000 with a minimum payment of $2,000 for eligible small and medium-sized businesses. The payment will provide cash flow support to businesses with a turnover of less than $50 million that employ staff, between 1 January 2020 and 30 June 2020. The payment will be tax free. This measure will benefit around 690,000 businesses employing around 7.8 million people. Businesses will receive a credit of 50% of the tax withheld in their activity statement from 28 April with refunds to be paid within 14 days.
$1.3 billion to support small businesses to support the jobs of around 120,000 apprentices and trainees. Eligible employers can apply for a wage subsidy of 50 per cent of the apprentice’s or trainee’s wage for up to 9 months from 1 January 2020 to 30 September 2020. Where a small business is not able to retain an apprentice, the subsidy will be available to a new employer that employs that apprentice.
Stimulus payments to households to support growth
$4.8 billion to provide a one-off $750 stimulus payment to pensioners, social security, veteran and other income support recipients and eligible concession card holders. Around half of those that will benefit are pensioners. The payment will be tax free and will not count as income for Social Security, Farm Household Allowance and Veteran payments. There will be one payment per eligible recipient. If a person qualifies for the one off payment in multiple ways, they will only receive one payment.
Payments will be from 31 March 2020 on a progressive basis, with over 90 per cent of payments expected to be made by mid-April.
Assistance for severely-affected regions
$1 billion to support those sectors, regions and communities that have been disproportionately affected by the economic impacts of the Coronavirus, including those heavily reliant on industries such as tourism, agriculture and education. This will include the waiver of fees and charges for tourism businesses that operate in the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park and Commonwealth National Parks. It will also include additional assistance to help businesses identify alternative export markets or supply chains. Targeted measures will also be developed to further promote domestic tourism. Further plans and measures to support recovery will be designed and delivered in partnership with the affected industries and communities.
The Government is also offering administrative relief for certain tax obligations, including deferring tax payments up to four months. This is similar to relief provided following the bushfires for taxpayers affected by the coronavirus, on a case-by-case basis. The ATO will set up a temporary shop front in Cairns within the next few weeks with dedicated staff specialising in assisting small business. In addition, the ATO will consider ways to enhance its presence in other significantly affected regions to make it easier for people to apply for relief, including considering further temporary shop fronts and face-to-face options.
The Government maintains its economic support package is proportionate, timely and scalable to respond to the economic challenges presented by the spread of the coronavirus.
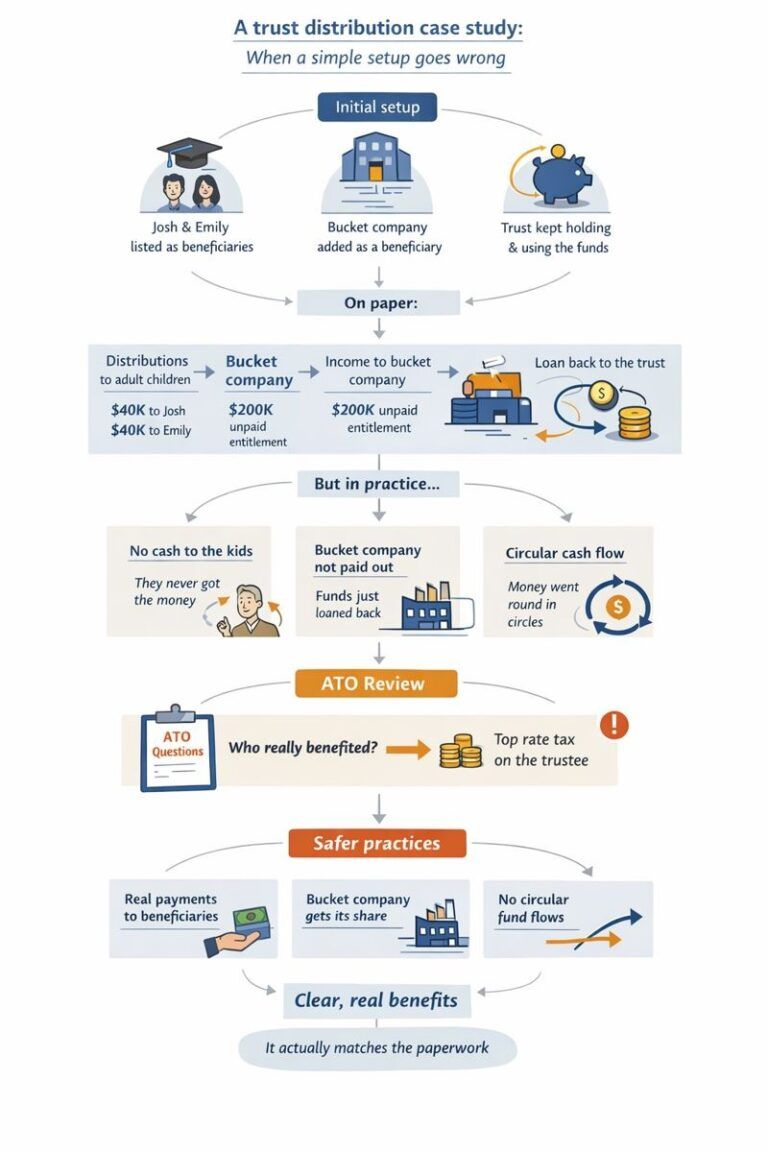
A real-world case study on trust distributions Mark and Lisa had what most people would describe as a “pretty standard” setup. They ran a successful family business through a discretionary trust. The trust had been in place for years, established when the business was small and cash was tight. Over time, the business grew, profits improved, and the trust started distributing decent amounts of income each year. The tax returns were lodged. Nobody had ever had a problem with the ATO. So naturally, they assumed everything was fine. This is where the story starts to get interesting. Year one: the harmless decision In a good year, the business made about $280,000. It was suggested that some income be distributed to Mark and Lisa’s two adult children, Josh and Emily. Both were over 18, both were studying, and neither earned much income. On paper, it made sense. Josh received $40,000. Emily received $40,000. The rest was split between Mark, Lisa, and a company beneficiary. The tax bill went down. Everyone was happy. But here’s the first quiet detail that mattered later. Josh and Emily never actually received the money. No bank transfer. No separate accounts. No conversations about what they wanted to do with it. The trust kept the funds in its main business account and used them to pay suppliers and reduce debt. At the time, nobody thought twice. “It’s still family money.” “They can access it if they need it.” “We’ll square it up later.” These are very common thoughts. And this is exactly where risk quietly begins. Year two: things get a little more complicated The next year was even better. They used a bucket company to cap tax at the company rate. Again, a common and legitimate strategy when used properly. So the trust distributed $200,000 to the company. No cash moved. It was recorded as an unpaid present entitlement. The idea was that the company would get paid later, when cash flow allowed. Meanwhile, the trust needed funds to buy new equipment and cover a short-term cash squeeze. The trust borrowed money from the company. There was a loan agreement. Interest was charged. Everything looked tidy on paper. From the outside, it all seemed sensible. But economically, nothing really changed. The trust made money. The trust kept using the money. The same people controlled everything. The bucket company never actually used the funds for its own business or investments. This detail becomes important later. Year three: circular money without anyone realising By year three, things had become routine. Distributions were made to the kids again. The bucket company received another entitlement. Loans were adjusted at year-end through journal entries. What is really happening is a circular flow. Money was being allocated to beneficiaries, then effectively coming back to the trust, either because it was never paid out or because it was loaned back almost immediately. No one was trying to hide anything. No one thought they were doing the wrong thing. They were just following what they’d always done. This is how section 100A issues usually arise. Slowly, quietly, and without any single dramatic mistake.
Rental deductions maximisation strategies

